Table of contents
Docker
Docker is a set of platform as a service products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. So with Docker you will be able to Develop once and deploy anywhere.
Docker Architecture
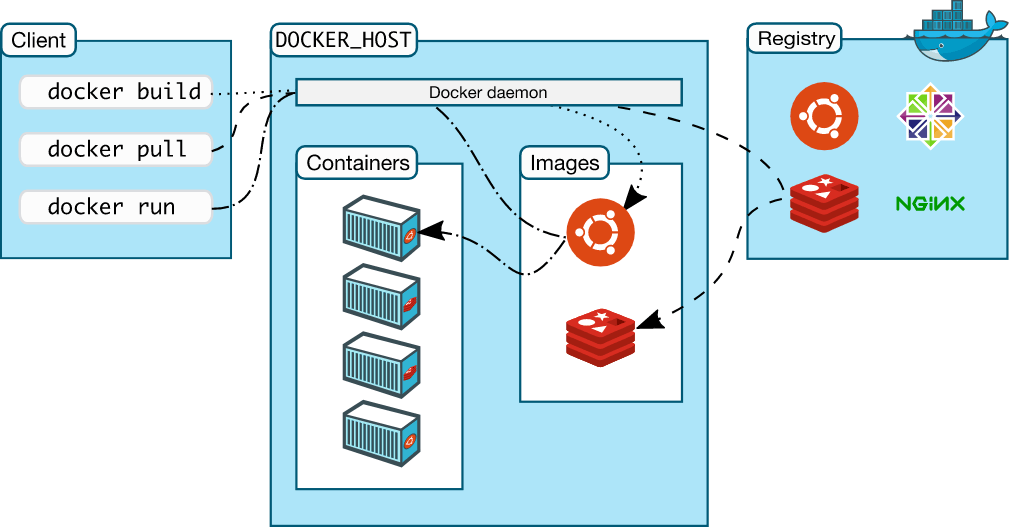
It is Client Server architecture
Docker Client:
It allows the user to communicate with docker host. It is local machine which talks to Docker Host. Docker client and host communicate with API requests.
It provides docker commands. Client can talk to more than one host.
Docker Host:
It listens for API requests from client. It manages docker images. It contains Docker Objects like Images, Containers, Volumes and Networks.
Registry(Docker Hub):
It is used to store docker images. Dockerhub is the default registry. We can create our own registries.
Docker image:
Images are the templates from which containers are built. Images can be built using a Dockerfile or found on public registries like DockerHub. Images can be built from other images.
Docker Container:
It can also be looked as a running instance of an image. Unlike images containers are able to accept data and commands.
Docker Installation
on Windows
Download installer file from https://docs.docker.com/desktop/install/windows-install/
Install it step by step
On Linux
Install docker using https://docs.docker.com/desktop/install/linux-install/
Docker Commands
docker run - Create and run a new container from an image
https://docs.docker.com/reference/cli/docker/container/run/
docker run <image-name>
docker exec - Execute a command in a running container
-d flag: for running the commands in the background.
-i flag: it will keep STDIN open even when not attached.
-e flag: sets the environment variables
docker exec [options]
docker ps - List containers
-a flag: shows us all the containers, stopped or running.
-l flag: shows us the latest container.
-q flag: shows only the Id of the containers.
docker ps #list all containers
docker ps -[options]
docker build - Build an image from a Dockerfile
docker build -t image_name:tag .
docker pull - Download an image from a registry
docker pull <image-name>
docker push - Upload an image to a registry images List
docker push <image-name>
docker images - List images
docker images
docker login - Log in to a registry
-p, --password - Password
--password-stdin -Take the password from stdin
-u, --username - Username
docker login [options] [server]
docker logout - Log out from a registry
docker logout [server]
docker search- Search Docker Hub for images
-f, --filter -Filter output based on conditions provided
--format -Pretty-print search using a Go template
--limit -Max number of search results
--no-trunc - Don't truncate output
docker search [options]
docker version - Show the Docker version information
docker version
docker info - Display system-wide information
docker info
docker stop - stops docker container
docker stop <container-id>
docker start - starts docker container
docker start <container-id>
docker rm - delete a container
-f flag: remove the container forcefully.
-v flag: remove the volumes.
-l flag: remove the specific link mentioned.
docker rm [options] <container name or container-id>
docker inspect - Debug docker containers
docker inspect
Use-Case
Explore and make use of your new found docker skills by playing around with a PHPMYADMIN image.
Lookup phpMyAdmin image on DockerHub
Pull phpMyAdmin image
Run the phpMyAdmin image with intended flags
Access the admin page in your browser
#pull phpmyadmin image from docker hub
docker pull phpmyadmin
#list out docker images
docker images
#copy image id and use it in run command
docker run -d -p 80:80 <image-id>
#list docker containers
docker ps
#Access the admin page in your browser