Docker Orchestration
Containerization provides an opportunity to move and scale applications to clouds and data centers. Containers effectively guarantee that those applications run the same way anywhere, allowing you to quickly and easily take advantage of all these environments. Additionally, as you scale your applications up, you need some tooling to help automate the maintenance of those applications, enable the replacement of failed containers automatically, and manage the roll-out of updates and reconfigurations of those containers during their lifecycle.
Tools to manage, scale, and maintain containerized applications are called orchestrators. One of orchestration tool is Docker Swarm.
Docker Swarm
The Docker container orchestration tool, also known as Docker Swarm, can package and run applications as containers, find existing container images from others, and deploy a container on a laptop, server or cloud (public cloud or private).Docker Swarm is a cluster of Docker hosts connected by an overlay networking for service discovery. A Docker Swarm includes one or more manager nodes and one or more worker nodes, as shown in Figure. In the Swarm mode, a Docker service is the unit of Docker containerization. Docker containers for a service created from a Manager node are deployed or scheduled across the cluster and the Swarm includes a built-in load balancing for scaling the services. The expected state for a service is declared on the manager, which then schedules the task to be run on a node. However, the worker node itself still pulls the image and starts the container.
Read more about docker-swarm
https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/
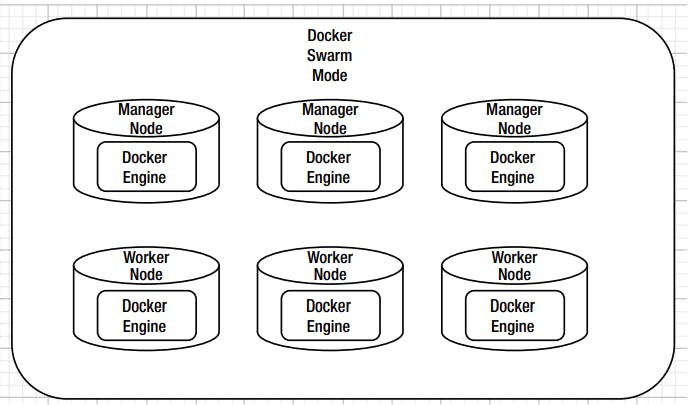
Nodes
An instance of a Docker host (a Docker Engine) is called a node. Two types of node roles are provided: manager nodes and worker nodes.
Manager Node
The manager node performs the cluster orchestration and manages the Swarm, including the initial scheduling of service tasks and subsequent reconciliation.
Worker Nodes
Worker nodes only increase the capacity of the Swarm to run service replica tasks
Promote Worker Node as Manager Node
You can promote a worker node to the manager role. This is useful when a manager node becomes unavailable or if you want to take a manager offline for maintenance. Similarly, you can demote a manager node to the worker role.
Use-case
Create a two-node Swarm cluster consisting of one manager node and one worker node.
Create 2 AWS ec2 instance. One for master node and one worker node.

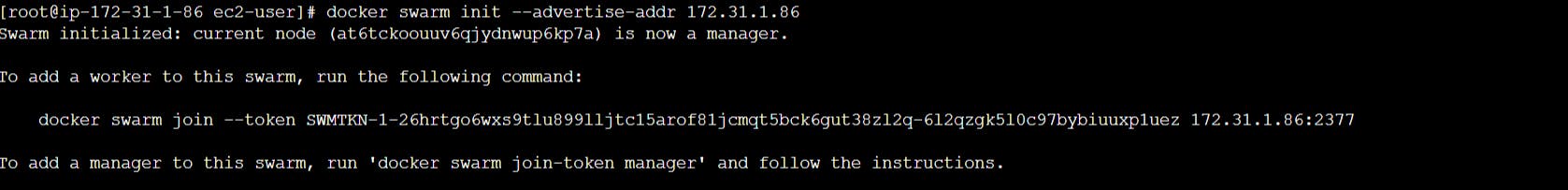
Initialize docker swarm in master node. The command to add a worker node is included in the output.
docker swarm init --advertise-addr <private Ip address of master node>
Open ports on all 3 nodes.
TCP port
2376for secure Docker client communication. This port is required for Docker Machine to work. Docker Machine is used to orchestrate Docker hosts.TCP port
2377. This port is used for communication between the nodes of a Docker Swarm or cluster. It only needs to be opened on manager nodes.TCP and UDP port
7946for communication among nodes (container network discovery).UDP port
4789for overlay network traffic (container ingress networking).TCP port
22to SSH into our instances remotelyTCP port 5000 and 5001 for application.
Copy the docker swarm join command to add a worker node to the Swarm.
docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-3ex8dqk74z8ybohksdqc22ri4jils7sf5dfjh471t4tsj9xqx9-ckpa8xc97v57ve2qw3zx132jj 172.31.47.168:2377

Use docker node ls command to list all nodes on master node.
#run this command on master ndoe
docker node ls

Clone example source code provided by docker as example-voting-app.
git clone https://github.com/docker/example-voting-app.git
cd example-voting-app
Copy and paste below code into docker-compose.yml file.
om here:
version: "3"
services:
redis:
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- "6379"
networks:
- frontend
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
db:
image: postgres:9.4
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- backend
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
vote:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_vote:before
ports:
- 5000:80
networks:
- frontend
depends_on:
- redis
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 2
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
result:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_result:before
ports:
- 5001:80
networks:
- backend
depends_on:
- db
deploy:
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
worker:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_worker
networks:
- frontend
- backend
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 1
labels: [APP=VOTING]
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
delay: 10s
max_attempts: 3
window: 120s
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
visualizer:
image: manomarks/visualizer
ports:
- "8080:8080"
stop_grace_period: 1m30s
volumes:
- "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
networks:
frontend:
backend:
volumes:
db-data:
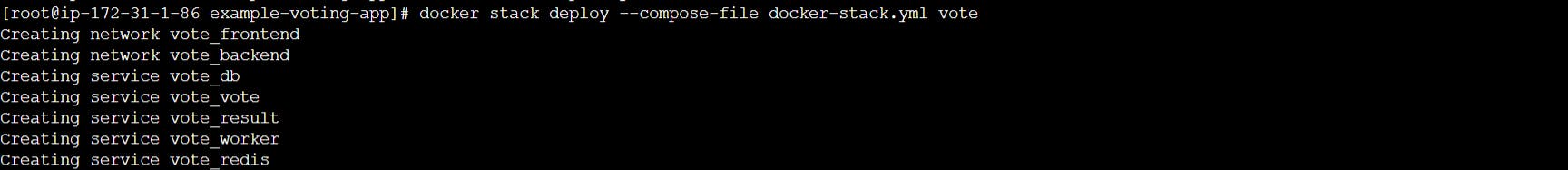
Create services using docker stack command and docker compose file. This will create 2 networks and 5 services. When we run docker stack command , it will create services on worker node as well.
docker stack deploy --compose-file docker-stack.yml vote
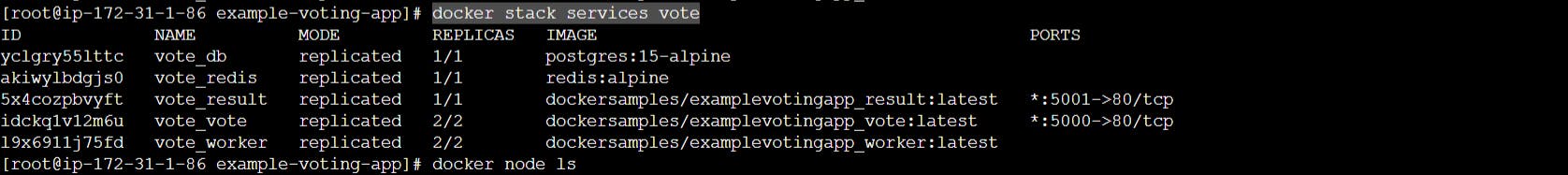
List running services on master node.
docker stack services vote
List running services on worker node.
docker ps

Verify running application using http://<public IP address>:5000. Application will run on both master node and worker node.
Remove the stack from docker swarm
docker stack rm vote
Promote worker node as manager node.
docker node promote <worker node name>
Demote manager node as worker node
docker node demote <Manager node name>
Leave the swarm
Run the docker swarm leave command on a node to remove it from the swarm.
docker swarm leave
If the node is a manager node, you receive a warning about maintaining the quorum. To override the warning, pass the --force flag. If the last manager node leaves the swarm, the swarm becomes unavailable requiring you to take disaster recovery measures.
After a node leaves the swarm, you can run docker node rm on a manager node to remove the node from the node list.
For instance:
docker node rm <Node-Name>
